3. Livestock & Manure Management
3.2. Manure management systems
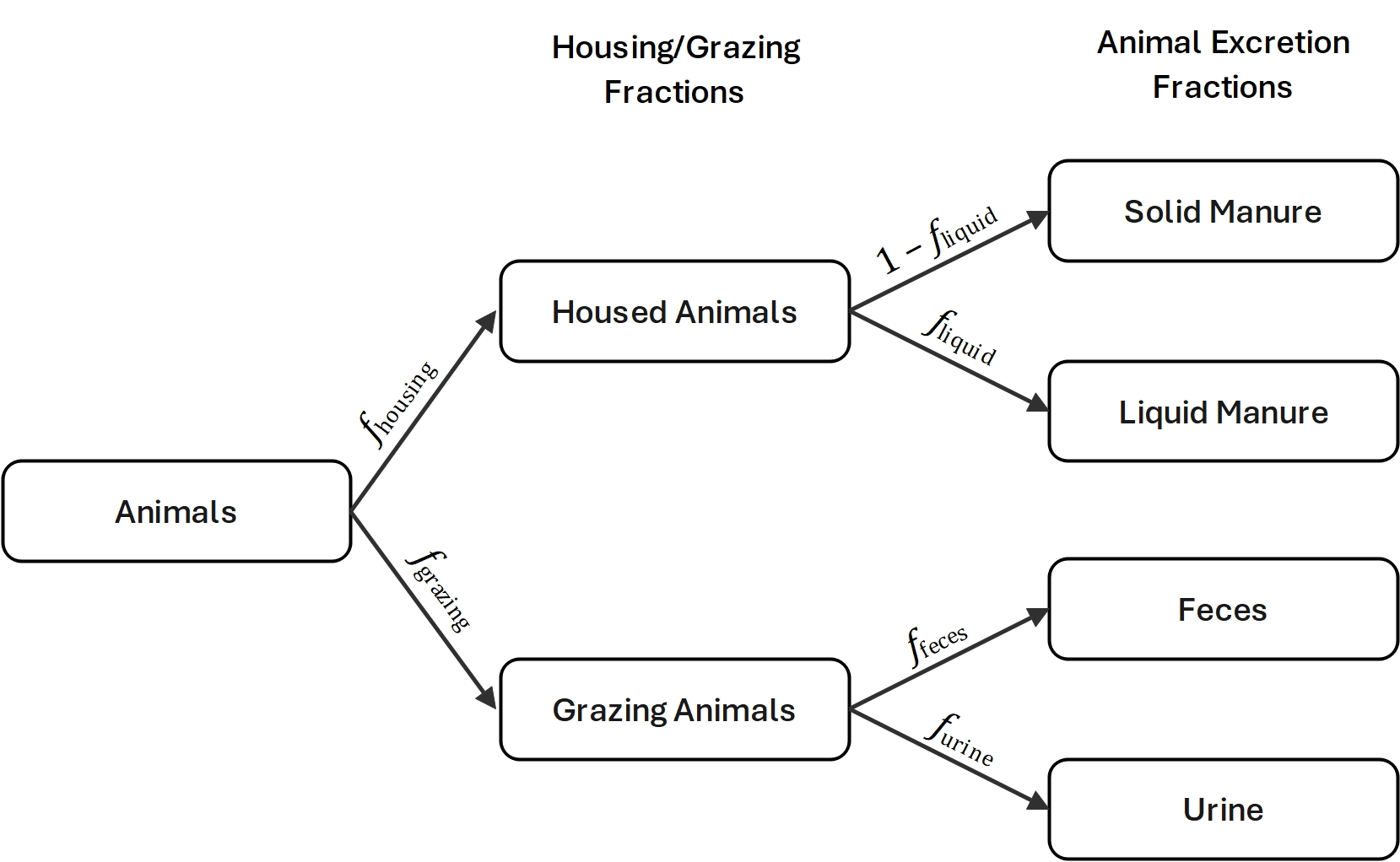
In Miterra, four types of manure management systems (MMS) are defined:
-
Housing: manure deposited during the period in stables and other roofed buildings.
-
Farmyard: manure deposited in the farmyard. A farmyard is the open area surrounding the farm buildings, where animals can stay for a short period during the day.
-
Storage: the storage of manure in unconfined piles/stacks, or in tanks/ponds/lagoons, typically for a period of several months to less than a year, before the manure may be applied to the field as fertilisers;
-
Grazing: the dung and urine deposited directly to the soil by grazing animals during grazing period.
The fractions of N excretions in each MMS (fhousing/yard/grazing) are derived from IPCC NIRs ( Greenhouse Gas Inventory Data - Flexible queries Annex I Parties).
For each MMS, livestock excretions are handled in both solid and liquid forms. The respective fractions of solid and liquid manure are determined by a predefined liquid-solid manure collection parameter (fliquid), which is specific to region and animal type.
3.3. N content in livestock excretion
N content in livestock excretion is calculated for each type of animal and each type of excretion (solid or liquid):
where:
|
is the annual amount of N excreted by the animals (kg N year–1). |
|
|
is the average amount of N in excretion that a single animal produces in one year (kg N head–1 year–1). |
|
|
is the total N content in solid/liquid fraction of manure from the housing/yard/grazing period (kg N). |
|
|
is the fraction of N excreted during housing, farmyard, or grazing period (unitless). |
|
|
is the fraction of solid or liquid manure collected for the livestock in a region (unitless). |
3.4. CH4 emissions
CH4 emissions originates from enteric fermentation, and manure methanogenesis during manure storage, and are calculated on the basis of animal numbers.
where:
|
is the CH4 emissions from enteric fermentation or during manure storage (kg CH4 year–1). |
|
|
is the emission factor of CH4 for enteric fermentation, or manure storage (kg CH4 head–1 year–1). |